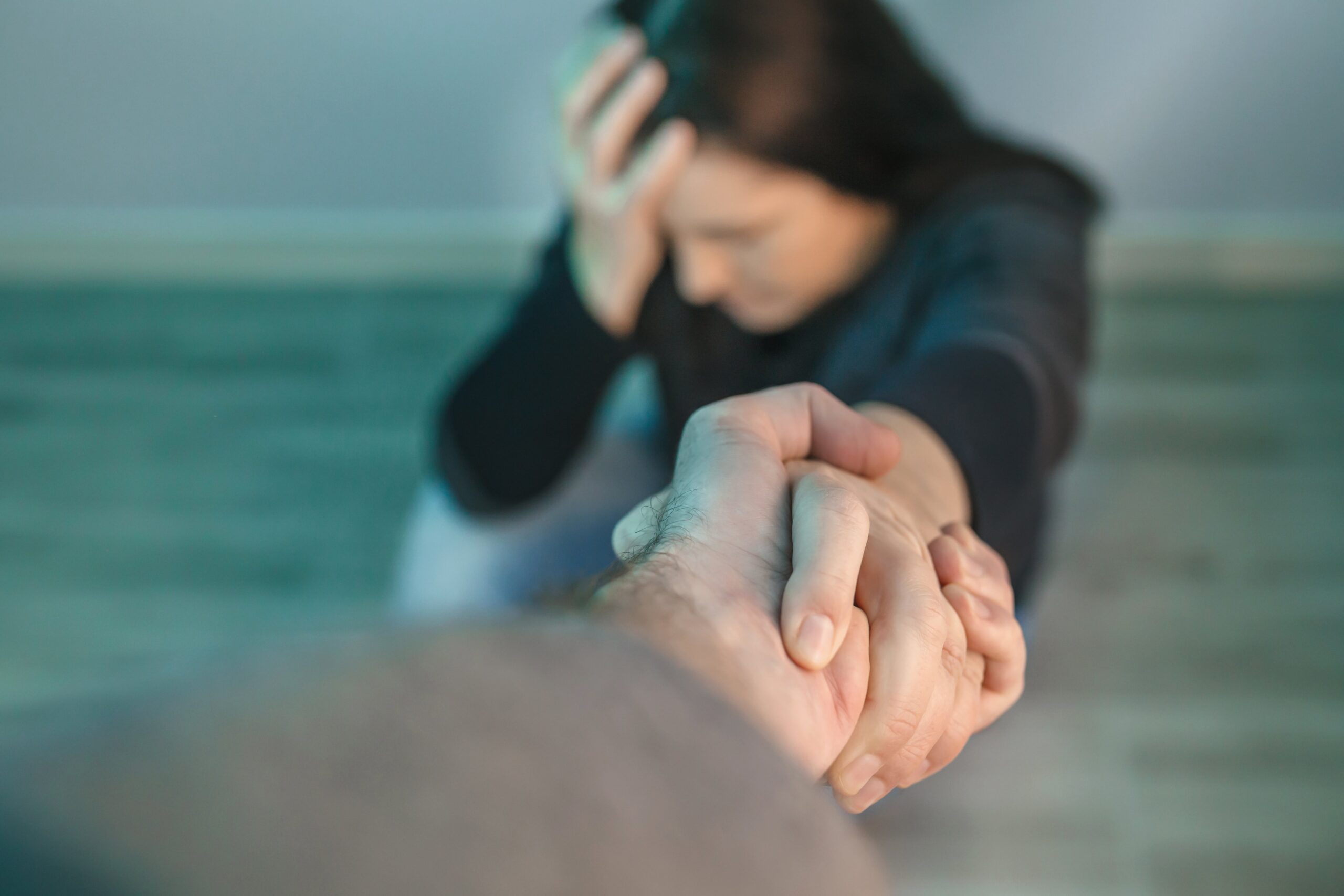
Seeking help for addiction is often a journey fraught with obstacles and internal struggles. It’s a challenge that transcends the physical aspects of dependence, delving deep into emotional, psychological, and societal dimensions. Acknowledging the need for assistance is the first step toward recovery, yet the path forward can be daunting. Here are six pivotal reasons that underscore the challenges individuals face when seeking help for addiction:
1. Stigma and Shame
One of the most significant barriers to seeking help for addiction is the stigma surrounding it. Society’s perception of addiction often leads to feelings of shame and guilt in those affected. The fear of being judged or labeled as weak prevents many from reaching out for support. Breaking through this stigma requires a shift in societal attitudes toward addiction, emphasizing compassion and understanding rather than judgment and condemnation.
2. Denial and Self-Deception
Denial is a powerful defense mechanism that often accompanies addiction. Individuals might minimize the severity of their problem or convince themselves that they have control over their substance use. This self-deception creates a barrier to seeking help, as acknowledging the extent of the issue becomes challenging. Overcoming denial requires confronting uncomfortable truths and recognizing the need for external assistance.
3. Fear of Change and Uncertainty
The prospect of change can be intimidating, especially when it involves breaking away from ingrained habits and routines associated with addiction. Fear of the unknown and uncertainty about life without the substance can deter individuals from seeking help. It requires a leap of faith to believe that life in recovery can be fulfilling and rewarding. Still, this belief often emerges only after taking the initial steps toward seeking help.
4. Lack of Access to Resources
Access to treatment and support services varies widely, presenting a significant challenge for many individuals seeking help for addiction. Financial constraints, limited availability of specialized programs, and geographical barriers can hinder access to quality care. Addressing this challenge involves advocating for better accessibility to treatment facilities and support networks, ensuring that help is available to anyone who needs it.
5. Dual Diagnosis and Co-occurring Disorders
Often, addiction is not an isolated issue but coexists with mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or trauma. Treating addiction alongside these co-occurring disorders requires specialized care that addresses both aspects simultaneously. However, identifying and managing these intertwined conditions can complicate the treatment process, making it more challenging for individuals to seek appropriate help.
6. Reluctance to Let Go of Coping Mechanisms
For many individuals, substance use becomes a coping mechanism — a way to deal with stress, trauma, or emotional pain. Letting go of this crutch can evoke a sense of vulnerability and discomfort. The thought of facing life’s challenges without the substance can be overwhelming. Helping individuals develop alternative, healthier coping strategies is crucial in enabling them to navigate life without relying on addictive substances.
Practical Ways To Help Individuals Overcome These Challenges
Supporting someone through their journey to overcome addiction requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to assist without judgment. Here are practical ways family members and friends can help individuals tackle each of these six challenges:
Stigma and Shame
- Educate Yourself: Learn about addiction to understand its complexities and dispel misconceptions. This knowledge can help you provide non-judgmental support.
- Open Communication: Create a safe space for open conversations where individuals feel comfortable discussing their struggles without fear of being judged.
- Encourage Support Groups: Help them find communities or support groups where they can connect with others who have experienced similar challenges. Encouragement from peers can be incredibly empowering.
Denial and Self-Deception
- Express Concern with Empathy: Approach the individual with empathy and express genuine concern about their well-being. Avoid accusations or confrontations, as these might reinforce denial.
- Share Observations: Share specific instances or observations without judgment to help them recognize patterns of behavior that indicate a problem.
- Offer Resources: Provide information about addiction treatment options or suggest professional guidance without pressure.
Fear of Change and Uncertainty
- Emphasize Support: Assure them of your unwavering support throughout their journey. Knowing they have a support system can alleviate some fears associated with change.
- Highlight Success Stories: Share stories of individuals who have successfully overcome addiction. Hearing about others’ triumphs can inspire hope and belief in the possibility of recovery.
- Take Small Steps Together: Encourage small changes or steps towards seeking help. Accompany them to support groups or appointments to ease the transition.
Lack of Access to Resources
- Research Available Resources: Help them research treatment facilities, support groups, or counseling services that are accessible and fit their needs.
- Financial Support: Offer assistance in finding financial aid options, such as scholarships or low-cost treatment programs.
- Advocate for Accessibility: Support initiatives advocating for better accessibility to your community’s treatment and mental health services.
Dual Diagnosis and Co-occurring Disorders
- Encourage Professional Assessment: Urge them to seek professional evaluation for underlying mental health conditions. Offer to accompany them to appointments for moral support.
- Integrated Treatment Options: Help them find treatment facilities or programs that specialize in dual diagnosis to address both addiction and mental health concerns simultaneously.
- Emotional Support: Be understanding and patient as they navigate the complexities of managing both addiction and mental health. Offer emotional support without minimizing their struggles.
Reluctance to Let Go of Coping Mechanisms
- Explore Alternative Coping Mechanisms: Encourage activities that promote well-being and act as healthy distractions or coping strategies, such as exercise, mindfulness, or hobbies.
- Provide Emotional Support: Listen without judgment when they feel vulnerable or overwhelmed. Offering emotional support helps them feel understood and less alone.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge and celebrate their milestones in adopting healthier coping mechanisms, no matter how small. Positive reinforcement can reinforce positive behaviors.
When you’re supporting someone with addiction, it’s crucial to remember that change takes time, setbacks are common, and patience is vital. Your consistent support and encouragement can make a significant difference in their journey toward recovery. Contact us today if you or someone you love struggles with substance use challenges.

 Verify Insurance
Verify Insurance
 Toll Free Call
Toll Free Call