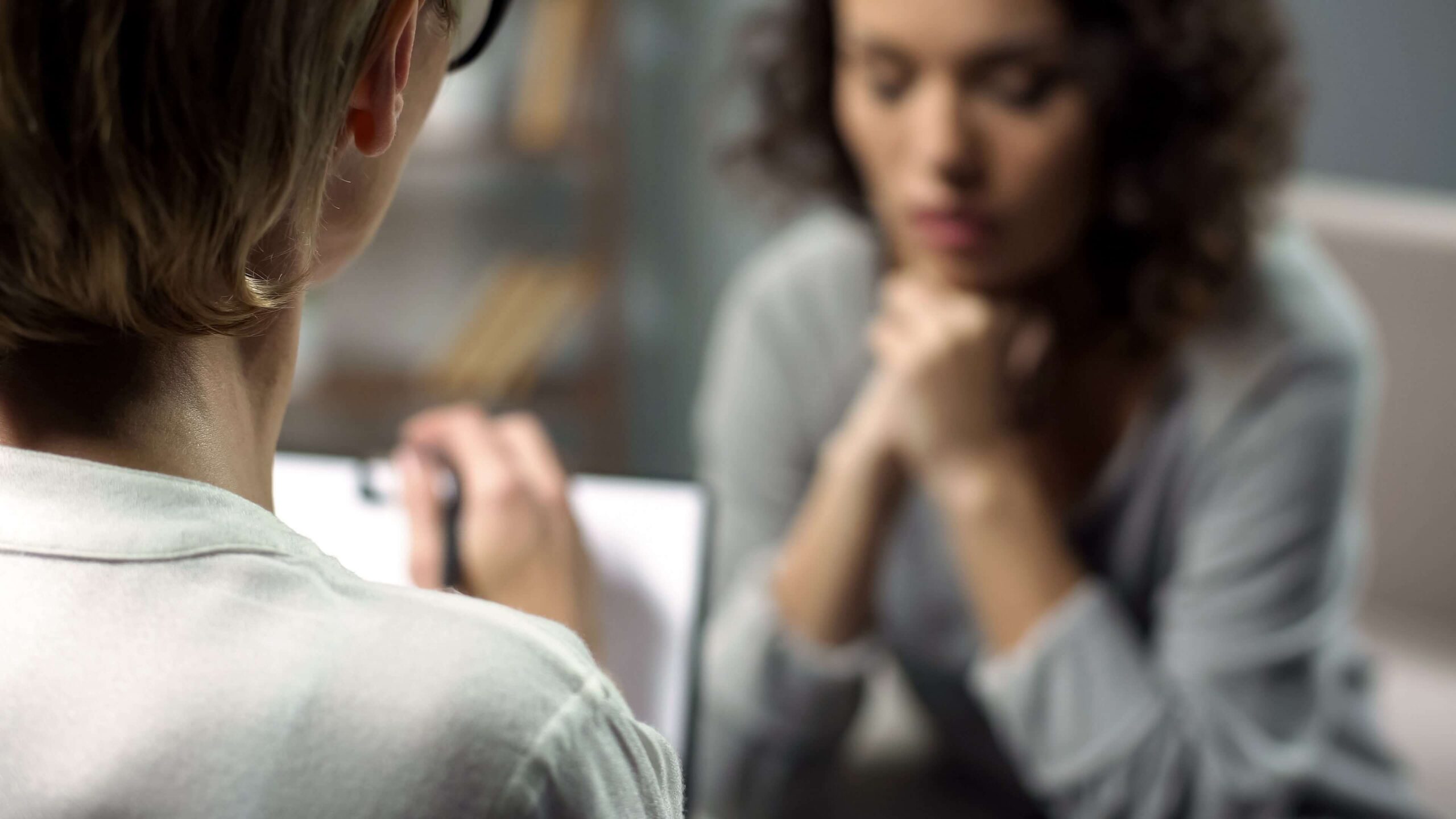
Most people who have struggled with addiction experience cognitive challenges and memory difficulties. That reality can be hard to live with, but there’s hope. Participating in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can not only help break the cycle of addiction, but it can also help improve and heal cognitive difficulties caused by substance abuse.
What Is CBT?
CBT is a therapeutic approach that aims to identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors. It has been successfully applied to various mental health disorders, including addiction. The basic premise of CBT is that thoughts influence feelings, which, in turn, influences behavior. In short, by thinking behavior, individuals can and will behave better.
CBT helps individuals recovering from addiction:
- Identify Triggers: CBT helps individuals recognize the specific triggers that lead to substance use. By identifying these triggers, individuals can develop strategies to avoid or cope with them more effectively.
- Challenge Cognitive Distortions: CBT helps individuals challenge negative thought patterns and addiction-related cognitive distortions. These distortions may include minimizing the negative consequences of substance use or believing they cannot overcome their addiction.
- Cope with Cravings: CBT equips individuals with practical coping skills to manage cravings for drugs or alcohol. By developing healthier coping mechanisms, individuals can reduce the likelihood of relapse.
- Improve Coping Skills: CBT teaches individuals various coping skills to deal with stress, anxiety, and other emotional triggers without substance use. These skills empower individuals to face challenges and emotional discomfort in a healthier way.
- Lessen The Risk Of Relapse: CBT effectively prevents relapse by providing individuals with tools to recognize and manage high-risk situations. Through relapse prevention strategies, individuals are better prepared to maintain their sobriety long-term.
- Foster Self-Empowerment: CBT emphasizes self-empowerment and personal responsibility in the recovery process. It helps individuals recognize they can make positive changes and take control of their lives.
- Enhance Self-Esteem: Addiction can erode self-esteem and self-worth. CBT works on improving self-esteem by challenging negative self-perceptions and building a more positive self-image.
How Does CBT Help Individuals Enhance Memory and Cognitive Functioning?
Cognitive behavioral therapy can also help individuals improve their cognitive functioning. While its primary focus is not on memory improvement, CBT can indirectly contribute to better memory functioning in certain situations. Here’s how.
In addiction recovery, CBT addresses cognitive challenges and works to improve memory recall through the following techniques:
- Cognitive Restructuring: CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and cognitive distortions. By challenging irrational beliefs, individuals can develop more positive and constructive thinking. Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns in CBT can improve cognitive functioning by promoting cognitive flexibility and adaptive thinking. By replacing irrational beliefs with more rational and constructive thoughts, individuals can develop healthier ways of processing information and responding to various situations. This shift towards positive and constructive thinking can lead to better problem-solving abilities, enhanced decision-making, and reduced cognitive biases, ultimately improving overall cognitive functioning and emotional well-being.
- Memory Enhancement Techniques: Therapists can introduce memory-enhancing exercises and strategies to help patients improve their memory recall abilities. These techniques may include visualization, association, and mnemonic devices. These memory-enhancing techniques improve cognitive functioning by stimulating various cognitive processes and neural pathways in the brain. Visualization activates the visual cortex, enhancing memory retention through vivid mental imagery. Association creates meaningful connections between new information and existing knowledge, strengthening neural pathways and facilitating easier retrieval of memories. Mnemonic devices and chunking aid working memory capacity by organizing information more structured and manageable, reducing cognitive load and promoting better memory recall.
- Addressing Trauma: CBT addresses underlying trauma, which may contribute to cognitive challenges and memory difficulties. By confronting and resolving unresolved trauma, individuals can experience cognitive improvements as their emotional healing promotes a healthier and more stable cognitive state.
- Reducing stress and anxiety: CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs contributing to stress and anxiety. Chronic stress and anxiety trigger the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can negatively impact the brain’s hippocampus, a region crucial for memory formation and retrieval. By managing stress and anxiety through CBT and other relaxation techniques, individuals can reduce cortisol levels and protect the hippocampus from damage, improving memory function. Additionally, lower stress levels create a more conducive environment for attention and focus, allowing for better encoding and recall of information.
- Enhancing focus and attention: CBT can help individuals improve their focus and attention by teaching them techniques to concentrate on the task and reduce distractions. CBT helps individuals improve their focus and attention by teaching them mindfulness and concentration techniques, such as deep breathing and guided imagery. By practicing these techniques, individuals can reduce distractions and stay more present in the moment, leading to better information processing. Improved focus allows the brain to process and consolidate information more effectively, leading to better memory retention and recall.
- Improving organization and planning: CBT can help individuals develop better organizational skills and strategies for planning and managing their daily activities. Being organized and having a clear plan can make it easier to remember tasks and information. CBT helps individuals develop organizational skills by breaking tasks into manageable steps and creating structured plans. By learning effective strategies for organizing and managing daily activities, individuals can reduce cognitive overload and enhance their ability to remember tasks and information. The clear structure and planning provided by CBT allow individuals to prioritize and allocate their cognitive resources more efficiently, leading to improved memory recall and overall cognitive functioning.
Addiction recovery is a complex journey that involves healing the body and mind. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven invaluable in addressing cognitive challenges and memory recall issues caused by addiction. By challenging negative thought patterns, enhancing memory recall techniques, and improving executive functions, individuals in recovery can regain cognitive clarity and build a foundation for lasting sobriety.
Contact us if you or someone you know is struggling with addiction. Our qualified mental health professionals can integrate CBT into the recovery process, providing invaluable support for a healthier, more fulfilling life.

 Verify Insurance
Verify Insurance
 Toll Free Call
Toll Free Call