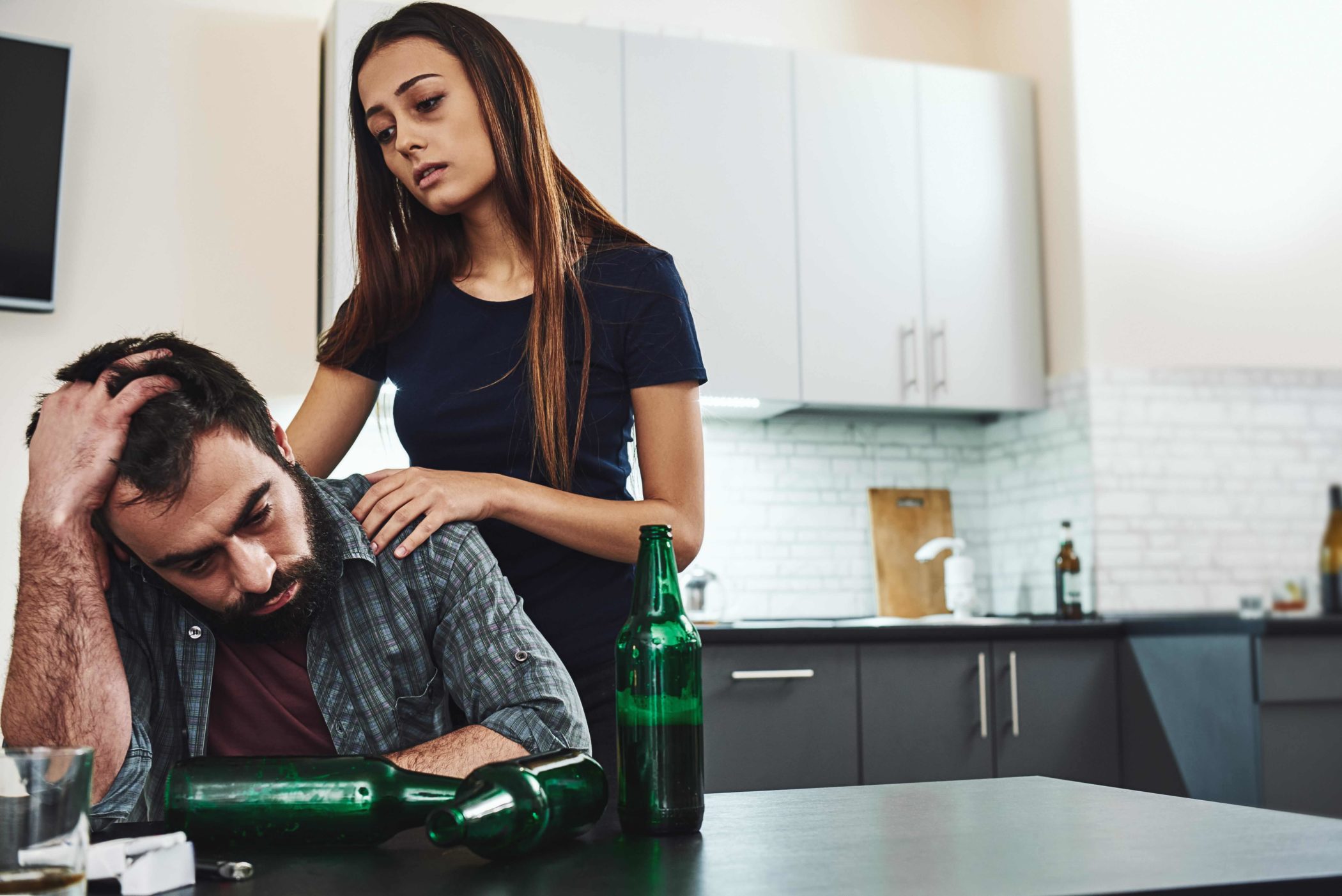
Codependency and addiction are two complex issues that frequently intertwine, leading to a mutually reinforcing and destructive cycle. Codependency is an unhealthy pattern of relating to others, marked by excessive reliance on external validation and a need to control or fix others. Addiction, on the other hand, involves compulsive dependence on substances or behaviors despite adverse consequences. Recognizing the interconnectedness of codependency and addiction is crucial in comprehending their impact and seeking practical solutions. Understanding the relationship between codependency and addiction is essential to facilitate healing, recovery, and the development of healthier, more balanced lives.
Signs Of Codependency
There are several signs and behaviors commonly associated with codependency. Some of the most common indicators of codependency in relationships influenced by addiction include:
- Excessive Caretaking: Individuals struggling with codependency often have an overwhelming need to care for others, even at the expense of their own well-being. They may prioritize other people’s needs above their own, feeling responsible for their happiness and making significant sacrifices to meet those needs.
- Difficulty Setting Boundaries: Codependents often have difficulty setting and maintaining healthy boundaries. They may have weak or nonexistent boundaries, allowing others to cross their limits and invade their personal space, emotions, or decisions.
- Fear of Abandonment: Codependents often have an intense fear of being abandoned or rejected. This fear can drive them to remain in dysfunctional or abusive relationships, even when they are aware of the negative consequences.
- Enabling Behavior: Codependents may enable others’ destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse, by protecting, covering up, or minimizing the consequences. They may also make excuses or rescue others from the natural consequences of their actions.
- Lack of Personal Identity: Codependents often define themselves through their relationships with others. They may struggle with identifying their own feelings, opinions, and goals outside of their role as a caretaker or supporter.
- Difficulty Expressing Emotions: Codependents may suppress their feelings, fearing that expressing them could lead to conflict or rejection.
How Can Addiction Lead To Codependency?
Addiction can indirectly contribute to codependency because of the dynamics that often emerge as a result of addictive behaviors such as manipulation, deceit, or emotional volatility, which can create a sense of chaos and instability. Codependent individuals can become enmeshed in this cycle, attempting to control or fix the addicted person’s behavior, often at the expense of their own well-being.
Oftentimes, addiction-induced codependency manifests itself as enabling. When this happens, codependent individuals support the addictive behavior by providing financial assistance, covering up consequences, or making excuses. This behavior generally stems from a deep fear of abandonment, a desire to maintain control or a belief that their self-worth is dependent on the well-being of the addicted person.
Codependent individuals and people struggling with addiction also often share underlying emotional issues, such as low self-esteem, shame, or unresolved trauma. As a result, the codependent individual may find validation or a sense of purpose in being needed by the addicted person, perpetuating a cycle of unhealthy reliance and enabling. In short, the addict “needs” the codependent, and the codependent “needs” the addict.
It is important to note that not all relationships involving addiction are codependent, and codependency can also exist without addiction. However, the combination of addiction and codependency can create a toxic dynamic that requires intervention and support for both parties to achieve healing and recovery.
The Dangers of Codependency
Codependency can be dangerous for several reasons, particularly for recovering addicts:
- Loss of Personal Identity. Codependency often involves a loss of personal identity as individuals become overly focused on meeting the needs of others. This can lead to a lack of self-awareness and self-care, making it difficult to establish and maintain healthy boundaries.
- Enabling Destructive Behavior. Codependents tend to enable and support the addictive behavior of their loved ones. By shielding the addict from consequences or providing resources to fuel their addiction, the codependent inadvertently contributes to the continuation of destructive patterns.
- Emotional Turmoil. Codependents may experience intense emotional turmoil due to their constant preoccupation with the well-being of the addict. This emotional rollercoaster can lead to anxiety, depression, and a compromised sense of self-worth.
- Stifling Personal Growth. Codependency can hinder personal growth and development. The codependent’s focus on meeting the needs of the addict can prevent them from pursuing their own goals, interests, and aspirations, leading to stagnation and a sense of unfulfilled potential.
- Relapse Risk. For recovering addicts, codependency poses a significant risk of relapse. The codependent’s behaviors and emotional dependence can trigger feelings of guilt, shame, and inadequacy in the recovering addict. Additionally, if the codependent continues to enable the addictive behavior, it becomes challenging for the addict to maintain sobriety in an environment that supports and encourages relapse.
It is crucial for recovering addicts to address codependency as part of their recovery process. By establishing healthier boundaries, developing self-esteem, and seeking support through therapy or support groups, individuals can break free from the dangers of codependency and enhance their chances of maintaining long-term sobriety and overall well-being.
How to Break Codependency and Overcome Addiction
Breaking codependency and overcoming addiction requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying emotional, psychological, and behavioral patterns.
Firstly, individuals must recognize and acknowledge their codependent and addictive tendencies, gaining awareness of how these patterns have influenced their lives. Then individuals need to seek professional help, such as therapy or counseling, which can provide invaluable support in identifying and addressing the root causes of codependency and addiction.
Developing healthy boundaries is also essential. Individuals grappling with codependency need to learn to prioritize self-care and assert their needs while detaching from an unhealthy reliance on others. Engaging in self-reflection, building self-esteem, and nurturing personal interests and goals can help break the cycle of codependency.
Additionally, participating in support groups or peer networks can provide a sense of community and understanding while receiving guidance from others who have successfully overcome codependency and addiction.
Lastly, maintaining a commitment to ongoing personal growth, self-awareness, and sobriety is key to sustaining long-term recovery and building healthier, more fulfilling relationships.
Why Choose Bridges Of Hope?
Our program helps individuals achieve long-term recovery. Our treatment philosophy is based on a comprehensive and integrated approach to addressing all issues related to substance use and mental health disorders.
We understand codependency and its connection to addiction and use evidence-based treatment to help individuals overcome both circumstances. Contact us today if you or a loved one are ready to work toward healthier relationships.

 Verify Insurance
Verify Insurance
 Toll Free Call
Toll Free Call